Multidimensional database kernel
Databases can be categorized based on how they organize and manage data:
Data is stored in two-dimensional tables (rows and columns), similar to spreadsheets. It is suitable for storing structured information such as customer lists, order records, and inventory. Common use cases include daily transaction processing systems (OLTP).
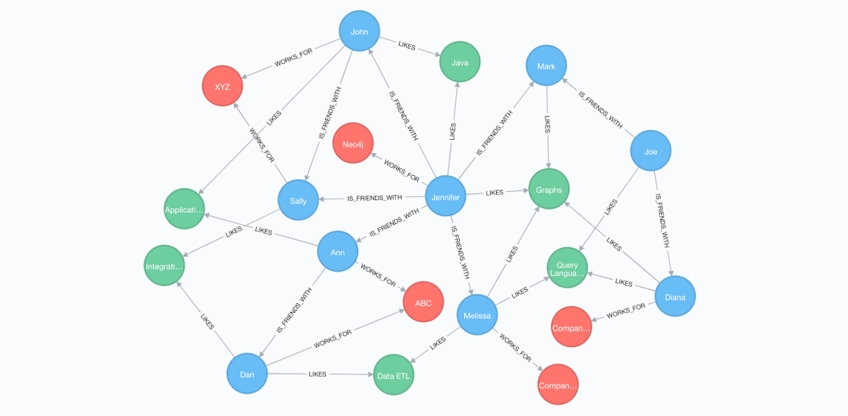
Data is organized using nodes and edges, emphasizing the relationships between entities—such as friendships, supply chains, or transaction links. It is well-suited for managing complex networks like social media, financial risk control, and fraud detection.
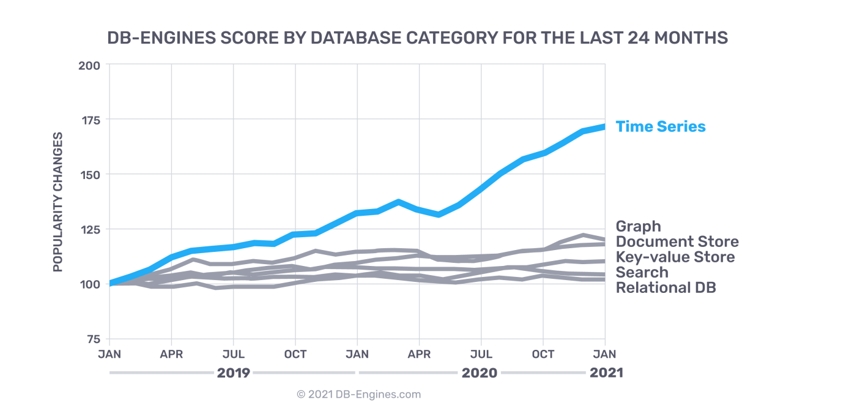
Specifically designed to record data in chronological order, like a timeline with continuously increasing data points. It is ideal for monitoring, log management, and collecting sensor data.
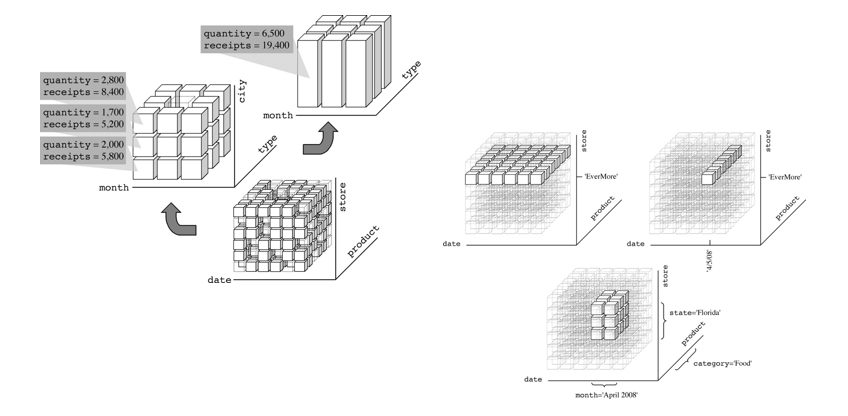
Data is structured as a hypercube in multidimensional space. Each axis represents a business dimension—such as region, date, organization, task, equipment, event, or status. Each data point corresponds to a specific coordinate in this space.
In a multidimensional database, we typically distinguish:
- Dimension: Analytical perspectives such as "Date," "Organization," or "Region."
- Measure: Numerical values to be calculated or aggregated, such as "Sales," "Inventory," or "Completion Rate."
Compared to relational databases, multidimensional databases offer distinct advantages in data analysis:
- Multi-perspective analysis: Freely combine dimensions for cross-analysis—e.g., viewing sales by region, month, and product category.
- Fast aggregation and drill-down: Flexibly move from high-level overviews to granular details—e.g., drilling from national sales to the daily sales of a product in a specific city.
- Effective decision support: Enables decision-makers to quickly identify trends, problems, and opportunities—especially when dealing with large and complex datasets.
Common application scenarios include:
- Sales analysis, financial analysis, and supply chain performance evaluation for enterprises
- Government resource planning and allocation
- Battlefield situation analysis in the defense sector
Multidimensional analysis is a key capability of OLAP systems, and it serves as the core benchmark for evaluating whether the system truly enables deep insight, complex decision support, and multi-scenario analysis.