This VSCode extension integrates jupytext's pairing and synchronization features, enabling automatic syncing between notebooks and their version-control-friendly text formats (.py, .md, etc.).
You can install this extension by searching for "jupytext-sync" in the Extensions Marketplace within your VSCode-like IDE.
The extension is available on both Microsoft VSCode Marketplace and on the Open VSX Registry in case you are using an alternative VSCode-based IDE like VSCodium.
Alternatively, you can install it directly by downloading the .vsix file from the release page on the GitHub and drag-and-drop it in your VSCode-based IDE. This has the downside that you will not be notified about available updates.
The extension activates when VS Code has finished starting up (onStartupFinished), so it should be available shortly after launch.
- Python: You need a Python installation.
- Jupytext: The
jupytextPython package must be installed in the Python environment used by the extension. - VS Code Microsoft Python Extension (Recommended): For the best experience with automatic Python environment detection, it is recommended to have the Microsoft Python extension installed (open in VSCode / open on marketplace).
This extension solves several common annoyances and provides handy features for a better Jupyter Notebook experience in VSCode:
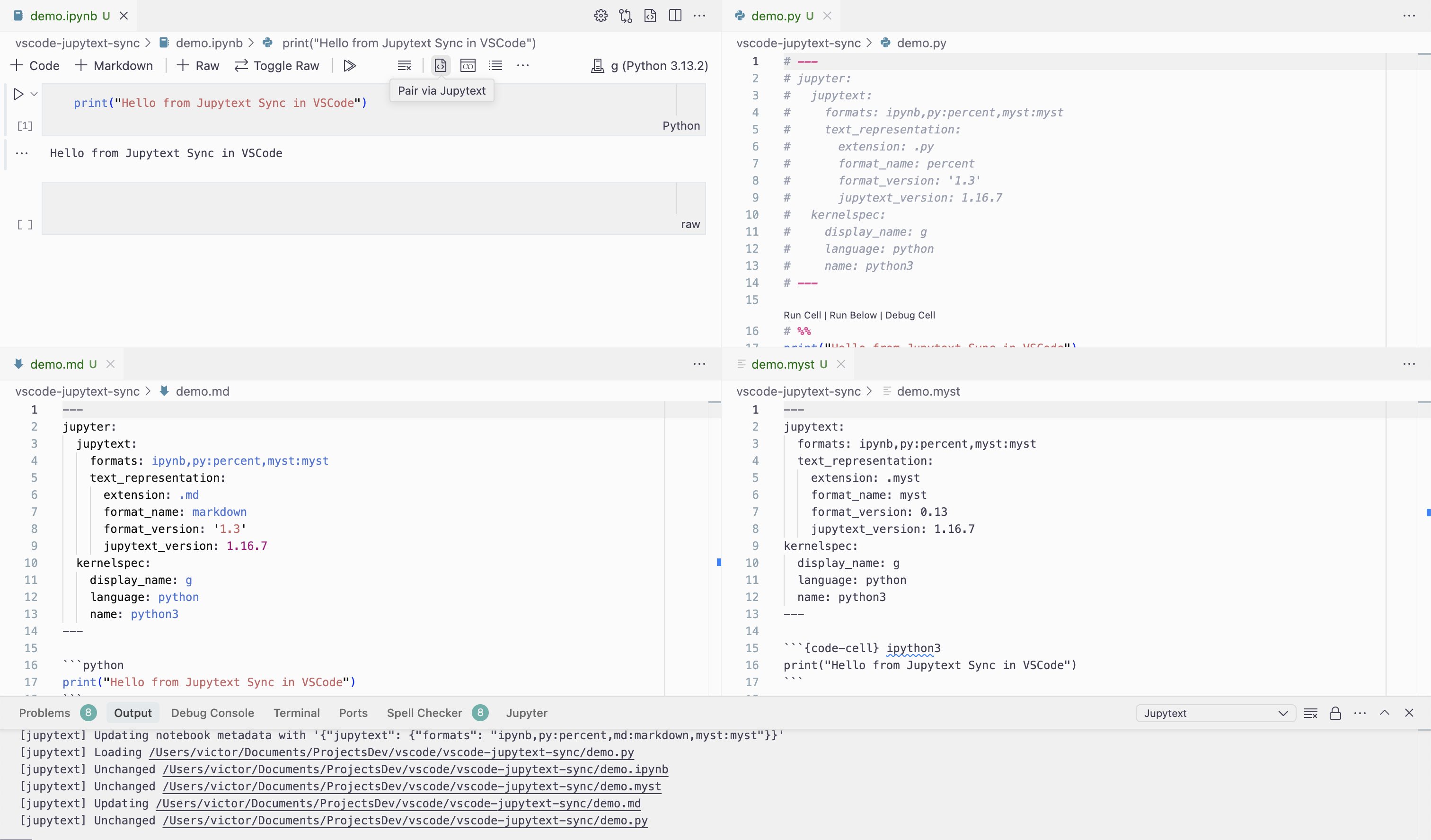
- Automatic Synchronization:
- Automatically syncs paired files (
.ipynband text-based formats like.py,.md) when you open, save, or close them. This ensures that your notebook and its text representation are always in sync. - Configuration options allow you to customize which events trigger a sync (on open, on save, on close for both text documents and notebook documents). See the
jupytextSync.syncDocumentssetting for details.
- Automatically syncs paired files (
- Seamless Notebook-First Workflow:
- Auto-open notebooks: When you open a paired text file (e.g.,
.py,.md), the extension can automatically open the paired.ipynbnotebook instead, providing a seamless editing experience. See the Editor Associations section below for configuration details. - Auto-cleanup: Optionally delete the
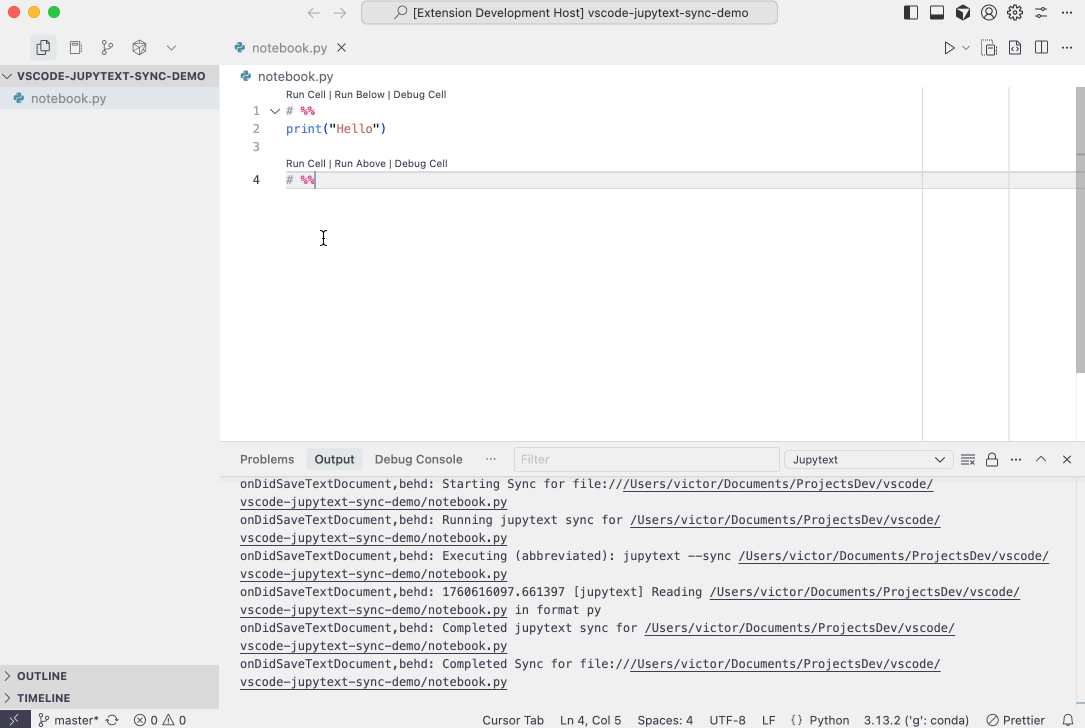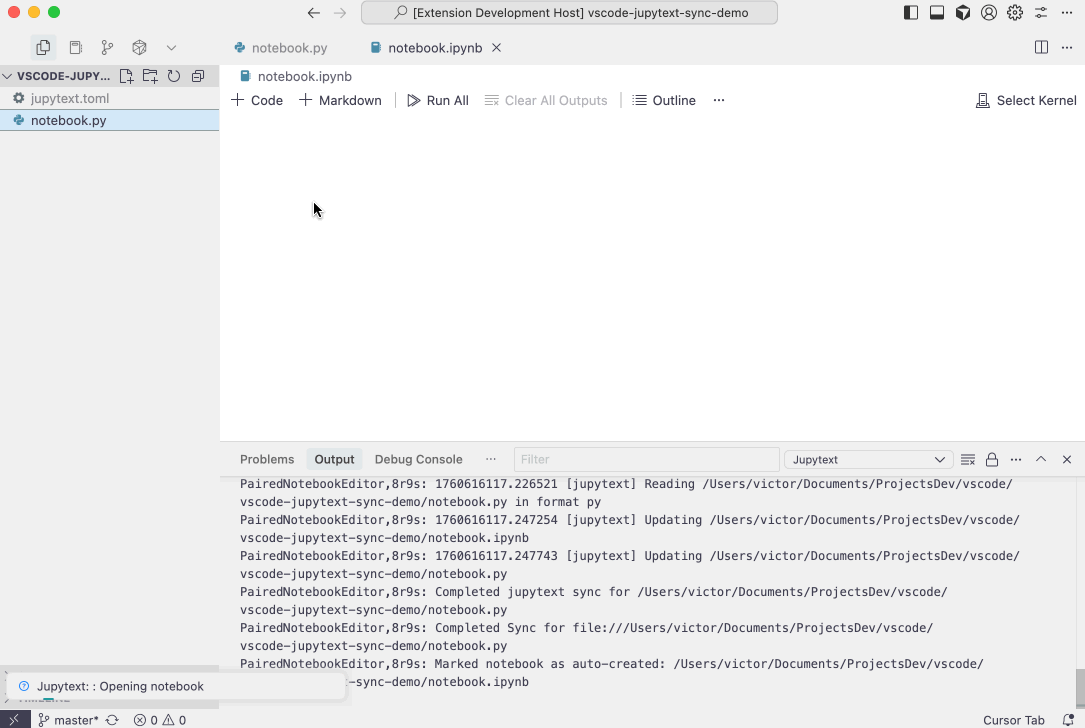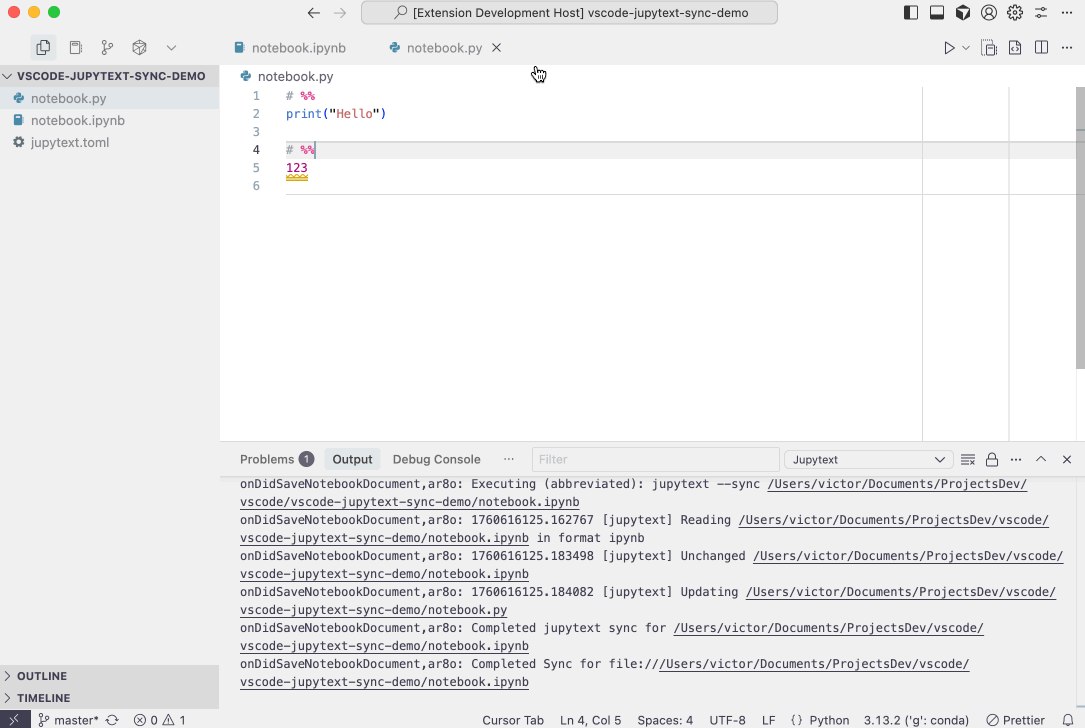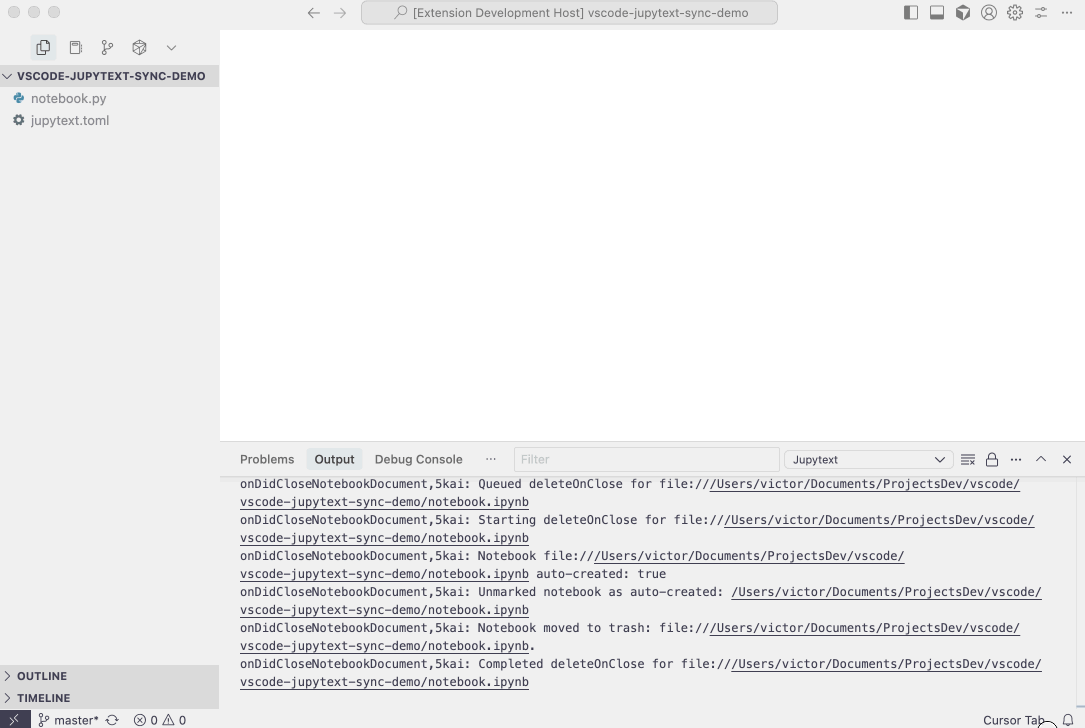
.ipynbfile when closing the notebook editor, keeping your workspace clean when the text file is your primary source of truth. Deleted files are moved to trash and can be recovered. This feature is opt-in. See thejupytextSync.deleteOnNotebookClosesetting for details.
- Auto-open notebooks: When you open a paired text file (e.g.,
- Open Text Files as Notebooks:
- Open Jupytext-compatible text files (e.g.,
.py,.mdwith Jupytext metadata) as notebooks using the "Open as paired Notebook via Jupytext" command. A notebook file will be created and all your edits in it will be synced to the text file(s).
- Open Jupytext-compatible text files (e.g.,
- Persistent Cell Outputs: All files are saved to disk, meaning cell outputs are not lost when reopening a notebook, providing a more consistent experience.
- Convenient Pairing Command: The "Pair via Jupytext" command is accessible from multiple convenient locations:
- Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P or Cmd+Shift+P)
- File Explorer context menu (right-click on a file)
- Editor context menu (right-click inside the editor or on the editor tab)
- Icons in the editor and notebook toolbars.
- Broad File Support: Supports all file extensions and formats recognized by your
jupytextinstallation. The extension dynamically fetches the supported formats fromjupytext. ThejupytextSync.defaultFormatssetting allows you to pre-configure default pairing strings for various extensions. - Raw Cells Support in Notebooks:
- Easily insert new raw cells via buttons in Notebook editor toolbar or keyboard shortcuts.
- Toggle cells to raw format and back to default code. Keyboard shortcuts available.
- Compact Notebook Layout: A command to apply a suggested VSCode settings for a more compact notebook layout, similar to traditional Jupyter interfaces.
- Python Interpreter Flexibility:
- Attempts are made to automatically discover Python executables that are able to invoke Jupytext. If the Microsoft Python extension is installed (open in VSCode / open on marketplace), its selected interpreter and other discovered environments (e.g.,
venv,conda) are considered. - Allows you to configure a custom Python executable path for
jupytextif needed (via thejupytextSync.pythonExecutablesetting). - You can use the "Jupytext: Locate Python and Jupytext" command or check the extension logs ("Jupytext: Show Jupytext Sync Logs" command) to see which Python environment is being used.
- Attempts are made to automatically discover Python executables that are able to invoke Jupytext. If the Microsoft Python extension is installed (open in VSCode / open on marketplace), its selected interpreter and other discovered environments (e.g.,
-
Pair your Notebook:
- Open an
.ipynbfile or a text file (e.g.,myscript.py,mymarkdown.md) that you want to use as a notebook. - Use the "Pair via Jupytext" command (accessible from the Command Palette, context menus, or toolbar icons).
- You'll be prompted to choose the Jupytext formats (e.g.,
ipynb,py:percent) unless disabled viajupytextSync.askFormats.onPairDocuments. The default suggestion is configurable per file extension usingjupytextSync.defaultFormats.
- Open an
-
Work in the Notebook:
- When you open your paired text file (e.g.,
.py,.md), the extension can automatically open the.ipynbnotebook for you (see the Editor Associations section below to configure this behavior). - The extension will automatically keep the paired files in sync upon saving (or other configured events via
jupytextSync.syncDocuments). - When you close the notebook, you can optionally have the
.ipynbfile automatically deleted (configurable viajupytextSync.deleteOnNotebookClose, which defaults to "never"), keeping your workspace clean while preserving your text file as the source of truth.
- When you open your paired text file (e.g.,
-
Version Control:
- Commit the text-based file (e.g.,
.py,.md) to your Git repository. This file is human-readable and diff-friendly. - Optionally, you can also commit the
.ipynbfile if you prefer to version control the outputs too. - If using auto-delete on close, consider adding
*.ipynbto your.gitignoreto avoid tracking generated notebook files.
- Commit the text-based file (e.g.,
-
Pre-commit Hook (Recommended): To ensure your paired files are always synchronized before committing, it's highly recommended to use the
jupytextpre-commit hook. This prevents accidental commits of unsynced files.Refer to the Jupytext documentation on pre-commit hooks for detailed configuration.
You can configure the extension's behavior via VSCode settings (search for jupytextSync in the Settings UI or edit your settings.json):
-
jupytextSync.pythonExecutable:- Description: The path to the Python executable used to invoke
jupytext. - Details: Jupytext Sync requires a Python executable with the
jupytextpackage installed.- Automatic discovery: If not specified, the extension attempts to find a suitable Python executable. If the Microsoft Python extension is installed, its selected interpreter and other known environments are checked. Otherwise, it looks for
pythonandpython3in your system PATH. The one providing the highestjupytextversion is preferred. - Manual override: Specify an absolute path or a command (e.g.,
python3). If using a command, ensure your VS Code instance inherits the correct PATH (launching from an activated terminal might be necessary for virtual environments).
- Automatic discovery: If not specified, the extension attempts to find a suitable Python executable. If the Microsoft Python extension is installed, its selected interpreter and other known environments are checked. Otherwise, it looks for
- Tip: Use the "Jupytext: Show Jupytext Sync Logs" or "Jupytext: Locate Python and Jupytext" commands to verify which Python executable is being used.
- Default:
""(empty string, for automatic discovery)
- Description: The path to the Python executable used to invoke
-
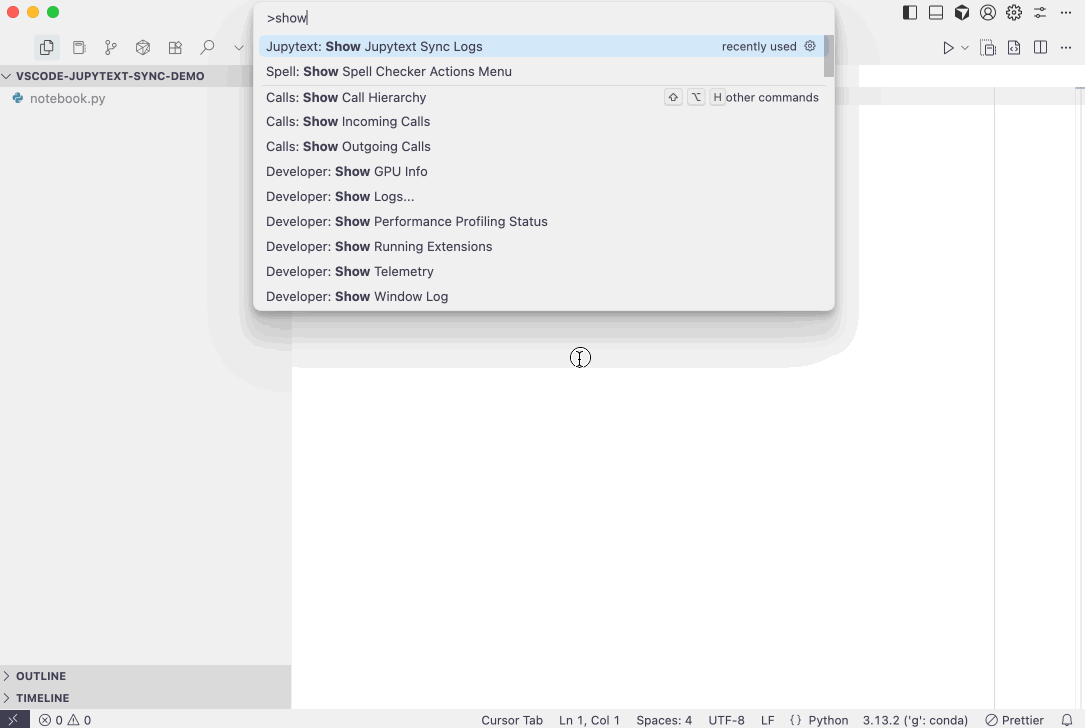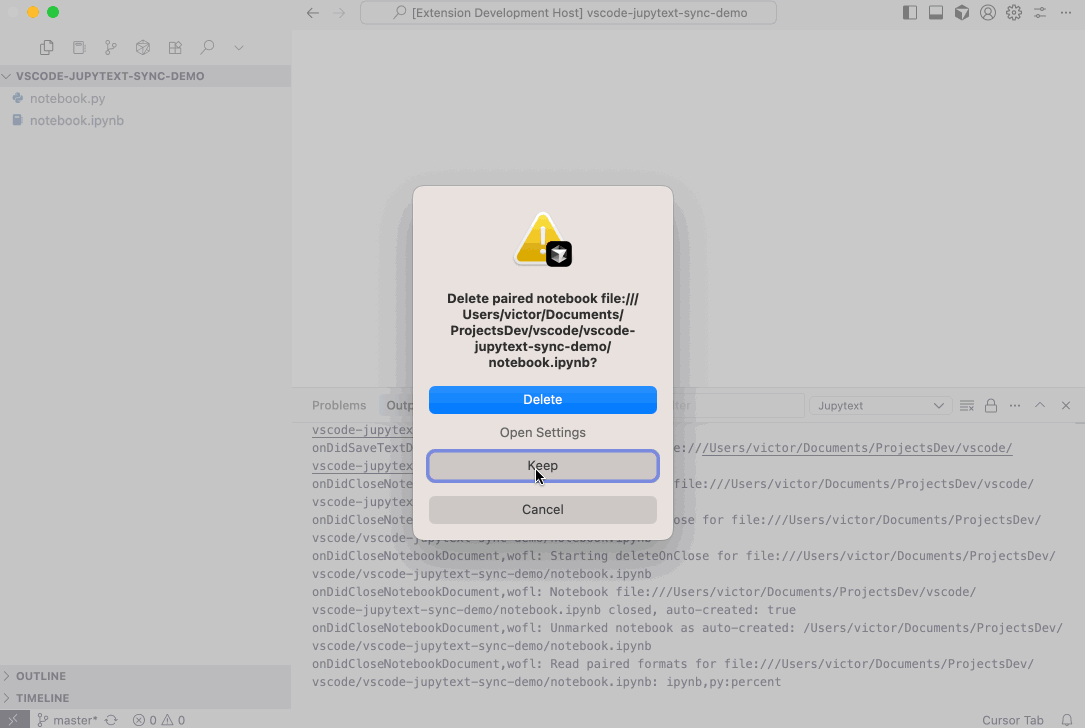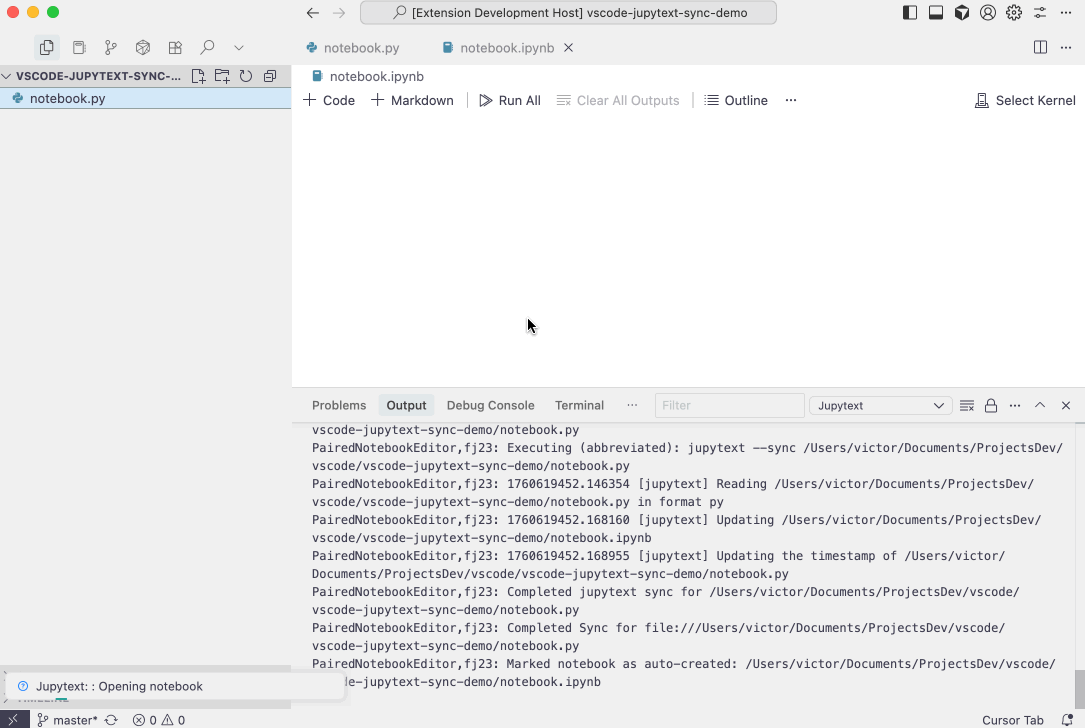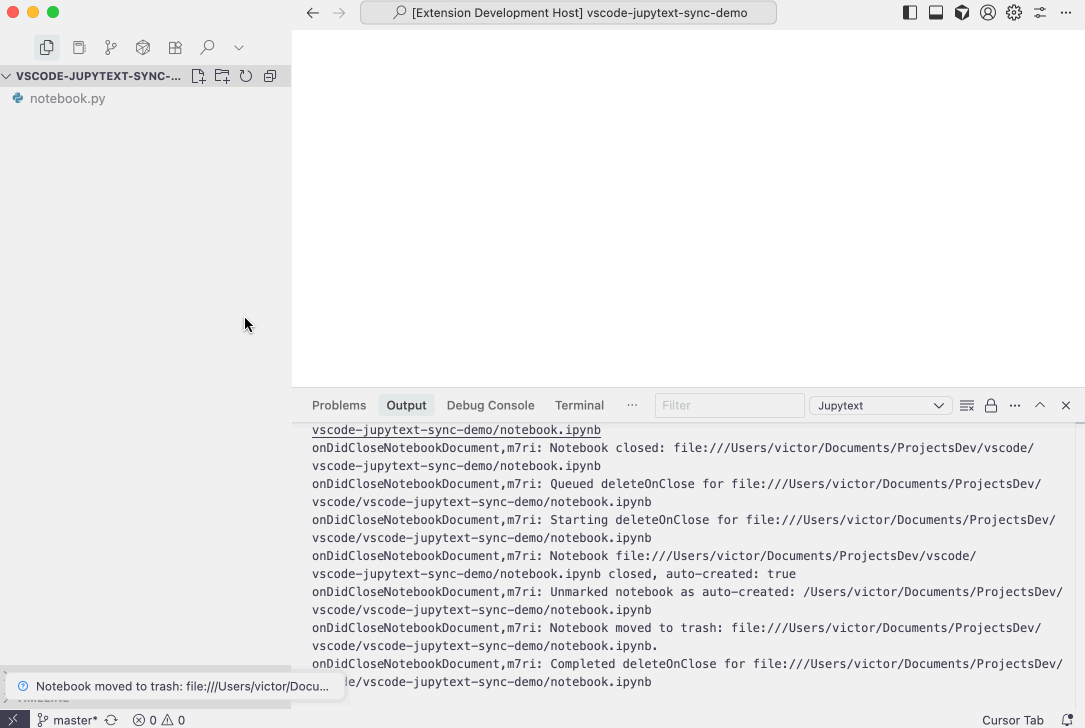
jupytextSync.deleteOnNotebookClose:- Description: Control whether to delete the
.ipynbnotebook file when closing a paired notebook editor. - Options:
"never": Never delete the notebook file when closing."ask": Always ask for confirmation before deleting."yes": Always delete if the notebook has paired formats."if auto created": Only delete if the notebook was auto-created by this extension via "Open as paired Notebook" or by opening a paired text file with the custom editor.
- Details: Deleted files are moved to the system trash/recycle bin and can be recovered. This feature is designed for workflows where the
.ipynbfile is generated from source text files (e.g.,.py,.md) and the text file is the primary source of truth. - Default:
"never"
- Description: Control whether to delete the
-
jupytextSync.syncDocuments:- Description: Controls on which events to attempt to
jupytext --syncpreviously paired documents. This applies even if pairing was done externally. - Properties:
onNotebookDocumentOpen(boolean): Sync when opening a notebook document.onNotebookDocumentSave(boolean): Sync when saving a notebook document. (Default:true)onNotebookDocumentClose(boolean): Sync when closing a notebook document.onTextDocumentOpen(boolean): Sync when opening a supported text document.onTextDocumentSave(boolean): Sync when saving a supported text document. (Default:true)onTextDocumentClose(boolean): Sync when closing a supported text document.
- Default: See individual property defaults above.
- Description: Controls on which events to attempt to
-
jupytextSync.askFormats:- Description: Controls whether to ask for pairing file formats before executing commands that may require pairing. If
false,jupytextSync.defaultFormatsare used. - Properties:
onOpenPairedNotebook(boolean): Ask for formats before opening a text document as a paired notebook. (Default:false)onPairDocuments(boolean): Ask for formats before pairing documents. (Default:true)
- Description: Controls whether to ask for pairing file formats before executing commands that may require pairing. If
-
jupytextSync.defaultFormats:- Description: Define default Jupytext pairing formats (e.g.,
ipynb,py:percent) used as suggestions or defaults. - Syntax: Uses Jupytext's
--set-formatsstring.${ext}can be used as a placeholder for the file extension (without the leading dot).defaultkey: An extension set to"default"in the configuration will inherit the format string from this key.- Subdirectories: Prefix with
dir_name//(e.g.,notebooks//ipynb,scripts//py:percent). Paths are relative to the source file's parent directory.
- Activation: Applies to file extensions recognized by your installed
jupytext. - Example Default Entry:
"default": "ipynb,${ext}:percent"
- Description: Define default Jupytext pairing formats (e.g.,
-
jupytextSync.setFormatsArgs:- Description: Customization for the command-line arguments of
jupytext --set-formatsinvocation. The order is preserved. - Examples:
["--set-formats"],["--set-formats", "--some-flag"] - Default:
["--set-formats"]
- Description: Customization for the command-line arguments of
-
jupytextSync.syncArgs:- Description: Customization for the command-line arguments of
jupytext --syncinvocation. The order is preserved. - Example:
["--sync", "--use-source-timestamp"] - Default:
["--sync"]
- Description: Customization for the command-line arguments of
-
jupytextSync.enabledMenus:- Description: Enable or disable Jupytext menus and buttons in various VS Code UI locations.
- Properties (all boolean, default
true):explorerContext: "Pair via Jupytext" in Explorer context menu.editorContext: "Pair via Jupytext" in Editor context menu.editorTitle: "Pair via Jupytext" button in Editor title bar.editorTitleContext: "Pair via Jupytext" in Editor title context menu.notebookToolbar: "Pair via Jupytext" button in Notebook toolbar.notebookToolbarInsertRaw: "Insert Raw Cell" button in Notebook toolbar.notebookToolbarToRaw: "Toggle Raw/Code Cell" button in Notebook toolbar.
The extension registers a custom editor (jupytextSync.pairedNotebookEditor) that allows you to automatically open paired text files as notebooks. You can control this behavior using VS Code's workbench.editorAssociations setting.
Via UI:
- Right-click a file (e.g.,
.pyor.md) in the Explorer - Select Open With...
- At the bottom of the available editors list, click Configure default editor for '*.py'... (or your file's extension)
- Choose Jupytext Paired Notebook (Beta) from the list
This will automatically configure the editor association for that file extension.
Via settings.json:
Alternatively, you can manually add the following to your VS Code settings to automatically open, e.g., .py and .md files as paired notebooks:
This tells VS Code to use the Jupytext Sync custom editor whenever you open a .py file. When the custom editor detects that the file is paired with a notebook (via Jupytext metadata), it will:
- Sync the paired files
- Open the paired
.ipynbnotebook instead
Note: If the text file is not paired with a notebook, or if Jupytext is not available, the file will automatically fall back to opening in the default text editor.
Even with editorAssociations configured, you can always open a file with the default text editor by right-clicking the file in the Explorer → Open With... → choosing the default text editor.
To configure Jupytext's own behavior (e.g., metadata filters, default formats), consult the official Jupytext documentation on configuring Jupytext via pyproject.toml or jupytext.toml files.
For example, to avoid noisy metadata in your text notebooks, you might add this to your pyproject.toml:
[tool.jupytext]
notebook_metadata_filter = "-kernelspec,-jupytext.text_representation.jupytext_version"
cell_metadata_filter = "-all"This extension provides the following commands, accessible via the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P or Cmd+Shift+P) under the "Jupytext" category:
Jupytext: Show Jupytext Sync Logs: Opens the output channel for Jupytext Sync, showing logs which can be helpful for troubleshooting, especially for Python executable discovery.Jupytext: Locate Python and Jupytext: Manually triggers Python and Jupytext discovery, showing detailed information about which Python executable and Jupytext version is being used. Useful for troubleshooting environment issues.Jupytext: Pair via Jupytext: Initiates the pairing process for the active file or a file selected from the Explorer. Prompts for Jupytext formats based onjupytextSync.askFormats.onPairDocumentsandjupytextSync.defaultFormats.Jupytext: Open as paired Notebook via Jupytext: Opens a Jupytext-compatible text file (e.g.,.py,.md) as a VS Code notebook. This is a key feature for working with text-based versions of notebooks.Jupytext: Insert Raw Code Cell Below and Focus Container: Inserts a new raw cell below the active cell in a notebook.Jupytext: Insert Raw Code Cell Above and Focus Container: Inserts a new raw cell above the active cell in a notebook.Jupytext: Change Cell to default Code: Changes the selected notebook cell(s) to the default code type.Jupytext: Change Cell to Raw Code: Changes the selected notebook cell(s) to raw format.Jupytext: Toggle Cell between Raw Code and default Code: Toggles the selected notebook cell(s) between raw and default code formats.Jupytext: Set Suggested Compact Notebook Layout: Applies a set of VS Code settings to achieve a more compact notebook UI.
The following keybindings are available when a notebook editor is focused and you are not currently typing in a cell input or output area:
y:Jupytext: Change Cell to default Coder:Jupytext: Toggle Cell between Raw Code and default Codet:Jupytext: Insert Raw Code Cell Below and Focus Containere:Jupytext: Insert Raw Code Cell Above and Focus Containeri i(pressitwice):jupyter.interruptkernel(VS Code built-in)0 0(press0twice):jupyter.restartkernel(VS Code built-in)
This extension was inspired by and builds upon the ideas from the following projects:
- marius311/jupytext-paired-vscode
- parmentelat/vscode-jupytext
- itself a soft fork of notebookPowerTools/vscode-jupytext
- with fixes from congyiwu/vscode-jupytext
- fmilanese-1/ds_utils: A VSCode extension that has some
jupytext-based capabilities and supports exporting notebooks to HTML vianbconvert, but does not include automatic synchronization of paired files.
{ "workbench.editorAssociations": { "*.py": "jupytextSync.pairedNotebookEditor", "*.md": "jupytextSync.pairedNotebookEditor" } }