English | 日本語
Important
v3 includes BREAKING CHANGES.
- Reference: Migration Guide from v2 to v3
- Reference: Migration Guide from v1 to v3
v2 and v1 will continue to be maintained and remain available for use.
Viewport Extra is a library that enables setting the minimum / maximum width of the viewport. It reduces the range of the viewport that needs to be considered when styling.
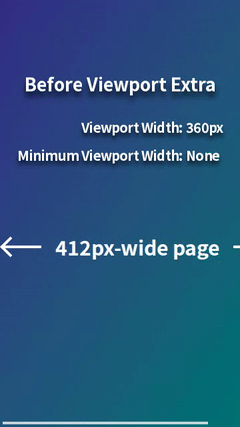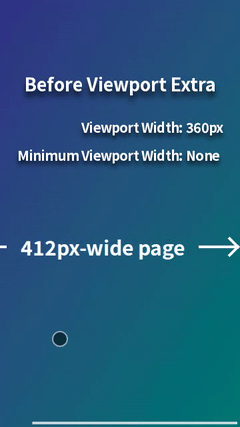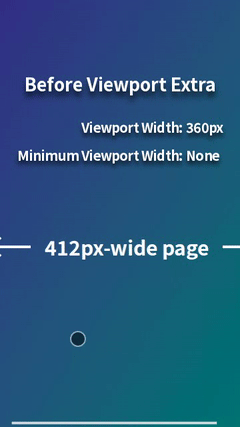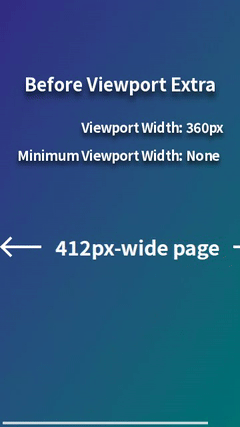
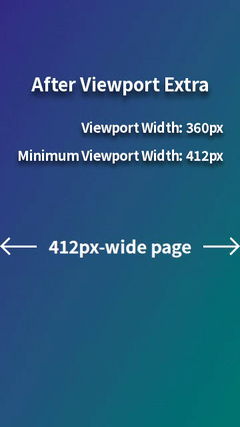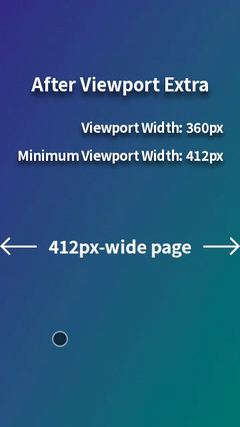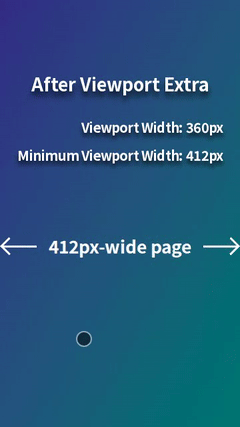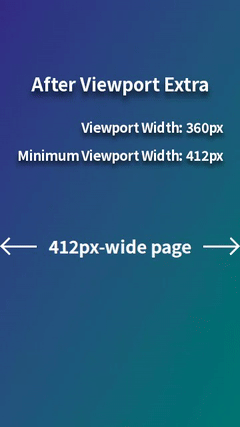
For example, when displaying a 412px-wide page on a mobile browser with a viewport width of 360px (e.g., Chrome on Galaxy S24 in portrait mode), horizontal scrolling occurs. This can be resolved by styling for viewport widths less than 412px, but it's a hassle. However, by using Viewport Extra to set the minimum viewport width to 412px, the page will be scaled down to fit perfectly within 360px, eliminating horizontal scrolling. This provides a simple solution with no styling required.
Page scaling is achieved by updating the content attribute of the <meta name="viewport"> element.
Viewport Extra supports asynchronous loading via the <script async> element or the import() syntax, ensuring it does not interfere with other processes on the page. Additionally, Viewport Extra has no dependencies and its standard build is tiny, at less than 1KB (Brotli compressed).
- Scale Down Page on Small Viewport Widths
- Scale Up Page on Large Viewport Widths
- Set Different Minimum / Maximum Widths per Media Query
- Rescale Page When Viewport Width Changes
- Scale Page Even in Legacy Environments
- Scale Page Without Using
<meta name="viewport-extra">Element
Pages containing the following code are scaled down on mobile browsers with viewport widths less than 412px, but are not scaled down on other browsers. Whether to scale down is determined only once when the pages are displayed (Reference).
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<meta name="viewport-extra" content="minimum-width=412">
<script async src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/immediate/viewport-extra.min.js"></script>import("viewport-extra").then(({ apply }) => {
apply([{ content: { minimumWidth: 412 } }])
})initial-scale=0.8737864077669902,width=412
initial-scale=0.9538834951456311,width=412
initial-scale=1,width=device-width
initial-scale=1,width=device-width
initial-scale=1,width=device-width
Pages containing the following code are scaled up on mobile browsers with viewport widths greater than 393px, but are not scaled up on other browsers. Whether to scale up is determined only once when the pages are displayed (Reference).
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<meta name="viewport-extra" content="maximum-width=393">
<script async src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/immediate/viewport-extra.min.js"></script>import("viewport-extra").then(({ apply }) => {
apply([{ content: { maximumWidth: 393 } }])
})initial-scale=1,width=device-width
initial-scale=1,width=device-width
initial-scale=1.0483460559796438,width=393
initial-scale=1.8676844783715012,width=393
initial-scale=2.6055979643765905,width=393
Pages containing the following code are scaled down on mobile browsers with viewport widths less than 412px or between 744px (inclusive) and 1024px (exclusive), but are not scaled down on other browsers. Whether to scale down is determined only once when the pages are displayed (Reference).
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<meta name="viewport-extra" content="minimum-width=412">
<meta name="viewport-extra" content="minimum-width=1024" data-media="(min-width: 744px)">
<script async src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/immediate/viewport-extra.min.js"></script>import("viewport-extra").then(({ apply }) => {
apply([
{ content: { minimumWidth: 412 } },
{ content: { minimumWidth: 1024 }, media: "(min-width: 744px)" },
])
})initial-scale=0.8737864077669902,width=412
initial-scale=1,width=device-width
initial-scale=0.7265625,width=1024
initial-scale=1,width=device-width
Pages containing the following code determine whether to scale up or down not only when displayed but also when the viewport width changes. This is useful in scenarios such as switching between portrait and landscape modes on mobile devices or screen splitting on tablets.
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<script
async
src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/immediate/viewport-extra.min.js"
id="viewport-extra-script"
></script>
<script>
const updateViewportMetaEl = () => {
// To prevent infinite resizing
new ResizeObserver((_, observer) => {
observer.unobserve(document.documentElement)
window.addEventListener("resize", updateViewportMetaEl, { once: true })
}).observe(document.documentElement)
ViewportExtra.apply([
{ content: { minimumWidth: 412 } },
{ content: { minimumWidth: 744 }, media: "(min-width: 640px)" },
])
}
if (window.ViewportExtra) {
updateViewportMetaEl()
} else {
document
.getElementById("viewport-extra-script")
.addEventListener("load", updateViewportMetaEl)
}
</script>import("viewport-extra").then(({ apply }) => {
const updateViewportMetaEl = () => {
// To prevent infinite resizing
new ResizeObserver((_, observer) => {
observer.unobserve(document.documentElement)
window.addEventListener("resize", updateViewportMetaEl, { once: true })
}).observe(document.documentElement)
apply([
{ content: { minimumWidth: 412 } },
{ content: { minimumWidth: 744 }, media: "(min-width: 640px)" },
])
}
updateViewportMetaEl()
})initial-scale=0.9538834951456311,width=412
initial-scale=0.9865591397849462,width=744
The standard build used above includes ES2021 syntax and features in the Widely Available stage of the Web Platform Baseline as of the release of Viewport Extra v3.0.0. To ensure compatibility with environments that do not support these (e.g., iOS Safari < 16, Android Chrome < 108), the ES5 build can be used (Reference).
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<meta name="viewport-extra" content="minimum-width=412">
<script async src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/immediate/es5/viewport-extra.min.js"></script>import("viewport-extra/immediate/es5").then(({ apply }) => {
apply([{ content: { minimumWidth: 412 } }])
})initial-scale=0.9101941747572816,width=412
initial-scale=1,width=device-width
Pages containing the following code behave the same as the implementation using the <meta name="viewport-extra"> element.
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<meta name="viewport" data-extra-content="minimum-width=412">
<meta name="viewport" data-extra-content="minimum-width=1024" data-extra-media="(min-width: 744px)">
<script async src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/immediate/viewport-extra.min.js"></script>initial-scale=0.8737864077669902,width=412
initial-scale=1,width=device-width
initial-scale=0.7265625,width=1024
initial-scale=1,width=device-width
-
min-width/max-widthcan be used as alternatives tominimum-width/maximum-width. However, when both styles are mixed, behavior is not guaranteed, so only one style should be used.<meta name="viewport-extra" content="min-width=412,max-width=640">
Similarly,
minWidth/maxWidthcan be used as alternatives tominimumWidth/maximumWidth. As with the previous case, when both styles are mixed, behavior is not guaranteed, so only one style should be used.apply([{ content: { minWidth: 412, maxWidth: 640 } }])
-
Using the following style together is recommended to prevent browsers on small mobile devices from unexpectedly changing the text size (Reference).
body { -webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; }
-
When testing with developer tools of desktop browsers, mobile device simulation must be enabled and the viewport must be set to the desired size before navigating to a page that uses Viewport Extra. If the order is reversed, the browser may ignore the
initial-scalesetting of the<meta name="viewport">element. This behavior is specific to simulation in developer tools and does not occur in actual mobile browsers.