-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 10
Tracking
Rez can emit messages to an AMQP-compatible listener such as RabbitMQ whenever a context is resolved.
Table of contents
Estimated time: 10 mins
We're going to create a Python script that listens for whenever a context is resolved.
| Process A - Consumer | Process B - Producer |
|---|---|
$ rez env python-3 pika -- python consumer.py
[*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C
[x] Context was created by manima @ toy
Packages:
- pika
- platform
- arch
- rez
- python-3
[x] Context was created by manima @ toy
Packages:
- platform
- arch
- python
[x] Context was created by manima @ toy
Packages:
- platform
- arch
- python
- shiboken2
- PySide2 |
$ rez env python -- exit
$ rez env PySide2 -- exit |
The initial output from the consumer is from creating the context within which we run the consumer. The second one is coming from the right-hand side resolving for rez env python.
Let's go.
Before we begin, let's have a closer look at what kind of data is emitted.
$env:REZ_CONTEXT_TRACKING_HOST="stdout" # PowerShell
export REZ_CONTEXT_TRACKING_HOST=stdout # Bash
set REZ_CONTEXT_TRACKING_HOST=stdout # cmd$ rez env
# Output printed hereSpin up a RabbitMQ instance using any means necessary. For this guide, we'll be using Docker.
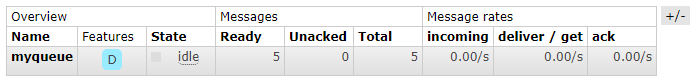
$ docker run -ti --rm --name rabbit -p 5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 --hostname rabbit rabbitmq:3.7-managementNow go to http://localhost:5672 and add a queue.
- Durable
Then add a exchange.
- Non-durable
- Fanout

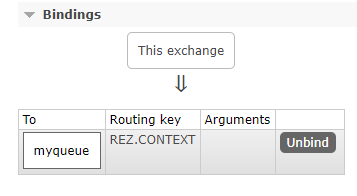
And then bind to it.
- Routing key:
REZ.CONTEXT
Now RabbitMQ is setup to listen for messages, it's time to get Rez to send some.
Rez doesn't emit any message until you tell about where to find your RabbitMQ instance.
rezconfig
context_tracking_host = 'localhost:5672'
context_tracking_amqp = {
"userid": "guest",
"password": "guest",
"exchange_name": "myexchange",
}Now try sending a few messages.
$ rez env -- exit
$ rez env -- exit
$ rez env -- exitYou should see 3 new messages in myqueue.
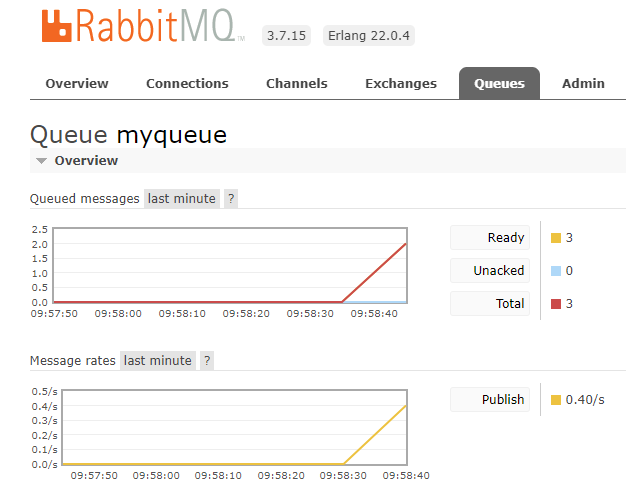
Now when you resolve an environment, a message is emitted to RabbitMQ. What we've got at the moment is akin to..
- Having written a letter (You, the
producer) - Delivering it to the post-office (RabbitMQ, the
exchange) - ...
What's missing is the post-office actually delivering it, and for that we need a consumer.
Prerequisites
You can use any suitable client to RabbitMQ, in this guide we'll use pika.
consumer.py
import pika
import json
def on_resolve(ch, method, properties, body):
payload = json.loads(body)
try:
context = payload["context"]
except KeyError as e:
print(" [x] Received %s" % body)
else:
print(" [x] Context was {action} by {user} @ {host}".format(**payload))
print(" Packages:")
for pkg in context["resolved_packages"]:
print(" - %s" % pkg["variables"]["name"])
param = pika.ConnectionParameters(host='localhost')
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(param)
channel = connection.channel()
channel.basic_consume(queue='myqueue',
on_message_callback=on_resolve,
auto_ack=True)
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()Now run it, like so.
$ rez env pika python -- python consumer.py
[*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C
[x] Context was created by manima @ toy
Packages:
- pika
- platform
- arch
- rez
- python
- localzReproducible software environments
for Windows, Linux and MacOS, written in and for Python
Feel free to edit this wiki
Guides
Table of Contents
- Home
- Getting Started
- Basic Concepts
- Shells
- Patch
- Configuring Rez
- Package Commands
- Package Definition Guide
- Variants
- Contexts
- Suites
- Building Packages
- Environment Variables
- Releasing Packages
- Rez GUI
- Command Line Tools
- Glossary
- Misc
Todo