An easy-to-use library for causal effect estimation using transformer-based in-context learning
🛠️ Installation • 🚀 Quick Start • 📊 Examples • 🔬 Reproducibility
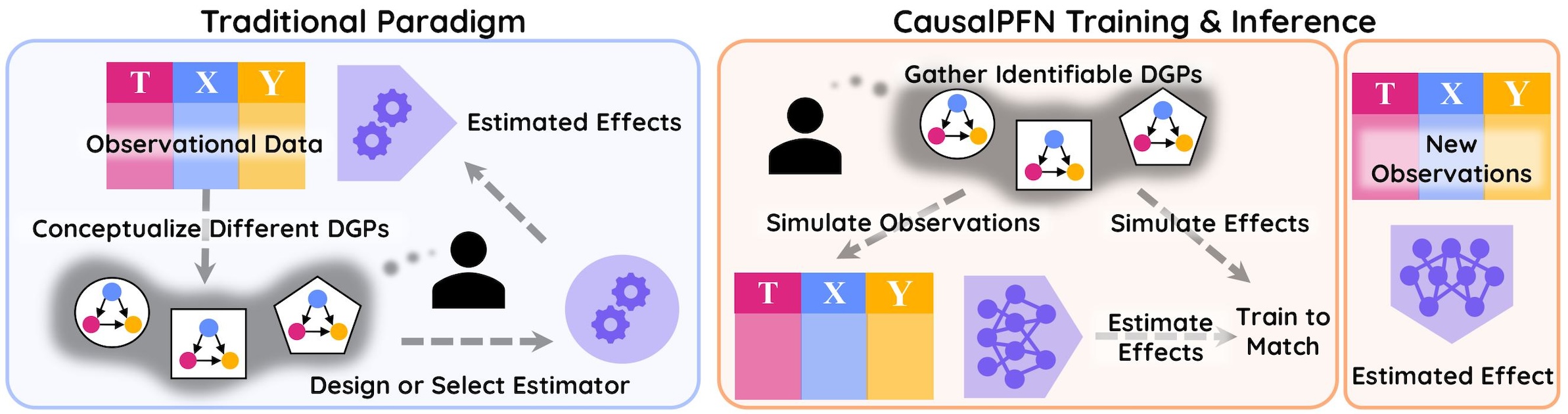
This library is is used to produce the results in our paper CausalPFN: Amortized Causal Effect Estimation via In-Context Learning.
CausalPFN leverages the power of transformer architectures for amortized causal effect estimation, enabling fast and accurate inference across diverse causal scenarios without the need for retraining. Our approach combines the flexibility of in-context learning with the rigor of causal inference.
- 🚀 Fast Inference: Amortized learning enables rapid causal effect estimation without retraining
- 🧮 Uncertainty Quantification: Built-in calibration and confidence estimation
- ⚡ GPU Accelerated: Optimized for modern hardware with CUDA support
- 📈 Benchmarked: Competitive performance against state-of-the-art causal inference methods
- 📊 Uplift-Modelling: Supports treatment effect estimation for personalized decision-making in real-world applications
pip install causalpfn- Python 3.10+
- PyTorch 2.3+
- NumPy
- scikit-learn
- tqdm
- faiss-cpu
- huggingface_hub
Here's a complete example demonstrating CausalPFN for causal effect estimation:
import numpy as np
import torch
import time
from causalpfn import CATEEstimator, ATEEstimator
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 1. Generate synthetic data
np.random.seed(42)
n, d = 20000, 5
X = np.random.normal(1, 1, size=(n, d)).astype(np.float32)
# Define true causal effects
def true_cate(x):
return np.sin(x[:, 0]) + 0.5 * x[:, 1]
def true_ate():
return np.mean(true_cate(X))
# Generate treatment and outcomes
tau = true_cate(X).astype(np.float32)
T = np.random.binomial(1, p=0.5, size=n).astype(np.float32)
Y0 = X[:, 0] - X[:, 1] + np.random.normal(0, 0.1, size=n).astype(np.float32)
Y1 = Y0 + tau
Y = Y0 * (1 - T) + Y1 * T
# 2. Train/test split
train_idx = np.random.choice(n, size=int(0.7 * n), replace=False)
test_idx = np.setdiff1d(np.arange(n), train_idx)
X_train, X_test = X[train_idx], X[test_idx]
T_train, Y_train = T[train_idx], Y[train_idx]
tau_test = tau[test_idx]
# 3. CATE Estimation
start_time = time.time()
causalpfn_cate = CATEEstimator(
device=device,
verbose=True,
)
causalpfn_cate.fit(X_train, T_train, Y_train)
cate_hat = causalpfn_cate.estimate_cate(X_test)
cate_time = time.time() - start_time
# 4. ATE Estimation
causalpfn_ate = ATEEstimator(
device=device,
verbose=True,
)
causalpfn_ate.fit(X, T, Y)
ate_hat = causalpfn_ate.estimate_ate()
# 5. Evaluation
pehe = np.sqrt(np.mean((cate_hat - tau_test) ** 2))
ate_rel_error = np.abs((ate_hat - true_ate()) / true_ate())
print(f"Results:")
print(f"ATE Relative Error: {ate_rel_error:.4f}")
print(f"PEHE: {pehe:.4f}")
print(f"CATE estimation time per 1000 samples: {cate_time / (len(X) / 1000):.4f}s")Explore our notebook collection below. Before running the notebooks, make sure to install the additional dependencies via pip install .[dev].
| Notebook | Description | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Causal Effect Estimation | Compare CausalPFN with baseline methods | CATE/ATE estimation, benchmarking |
| Hillstrom Marketing | Uplift modeling case study | Real-world marketing application |
| Calibration Analysis | Uncertainty quantification demo | Confidence intervals, calibration |
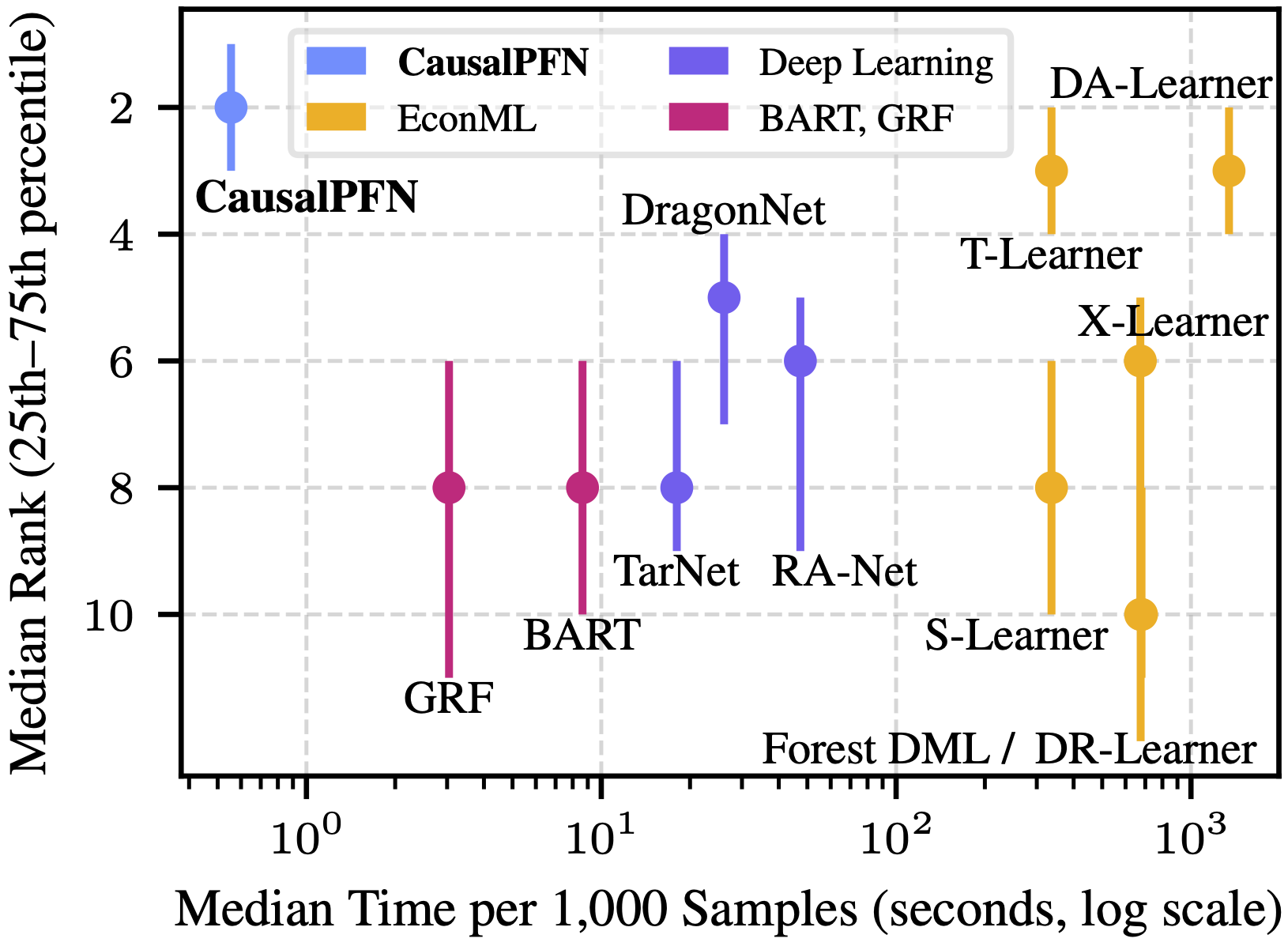
Time vs. Performance. Comparison across 310 causal inference tasks from IHDP, ACIC, and Lalonde. CausalPFN achieves the best average rank (by precision in estimation of heterogeneous effect) while being much faster than other baselines.
To fully reproduce the paper results, see the REPRODUCE file.
If you use CausalPFN in your research, please cite our paper:
@inproceedings{balazadeh2025causalpfn,
title={CausalPFN: Amortized Causal Effect Estimation via In-Context Learning},
author={Vahid Balazadeh and Hamidreza Kamkari and Valentin Thomas and Benson Li and Junwei Ma and Jesse C. Cresswell and Rahul G. Krishnan},
booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
volume = {38},
year = {2025}
}We welcome contributions! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch (
git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature) - Commit your changes (
git commit -m 'Add amazing feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin feature/amazing-feature) - Open a Pull Request
This project is licensed under the Apache-2.0 License - see the LICENSE file for details.
⭐ Star us on GitHub • 🐛 Report Bug • 💡 Request Feature
Made with ❤️ for better causal inference